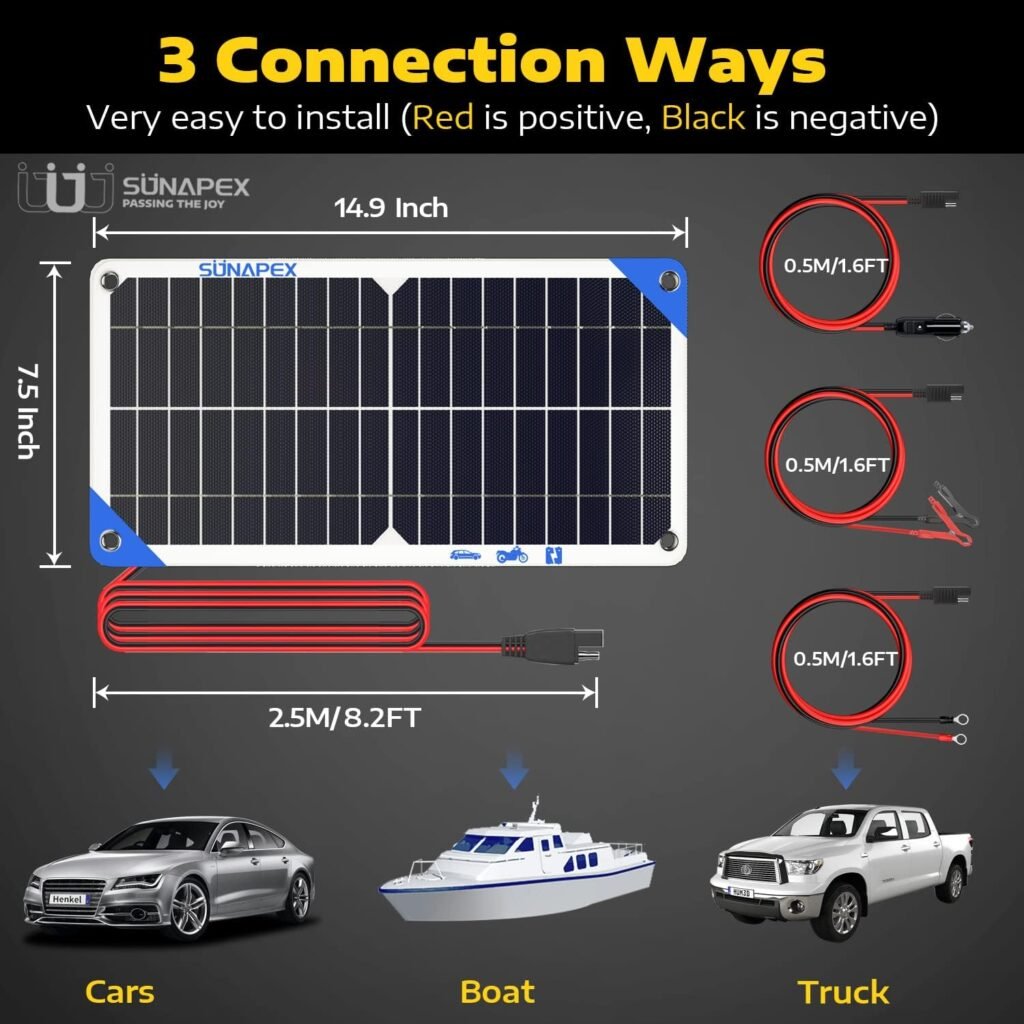
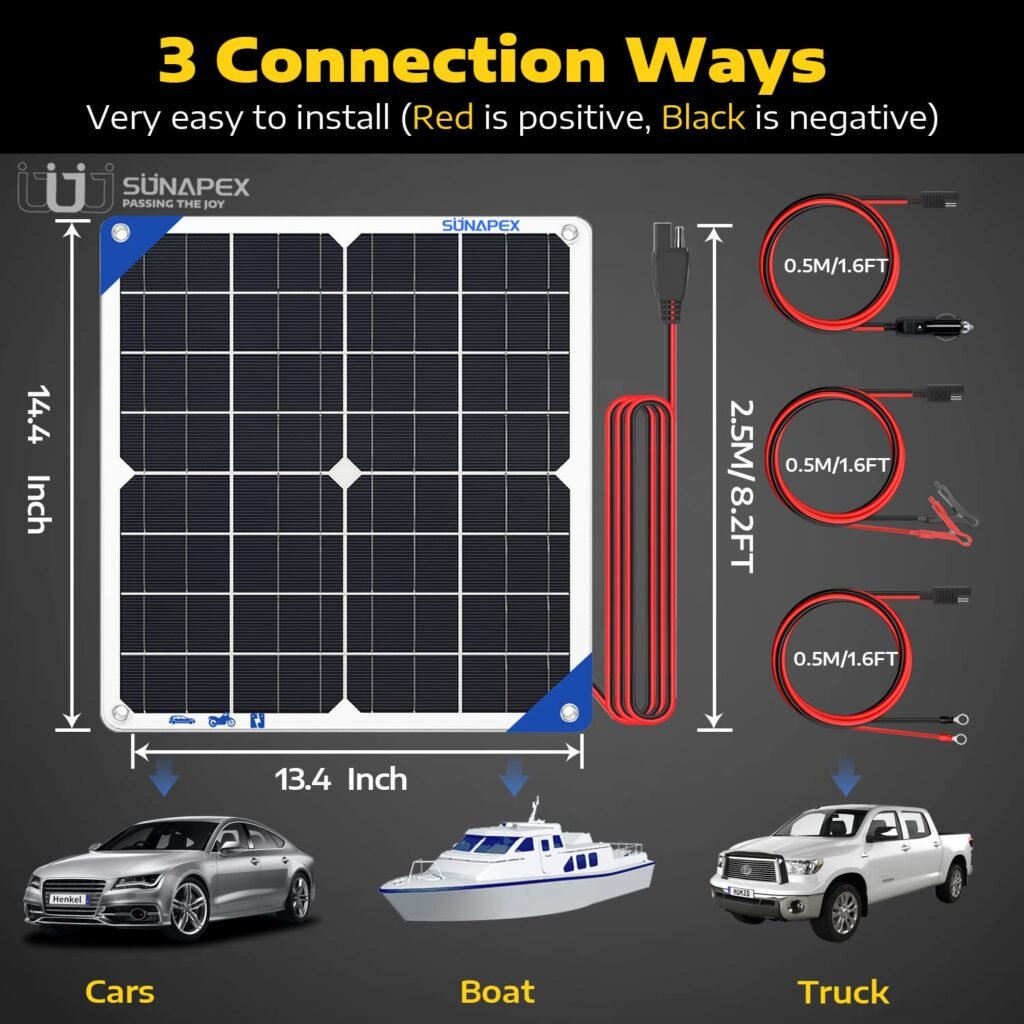
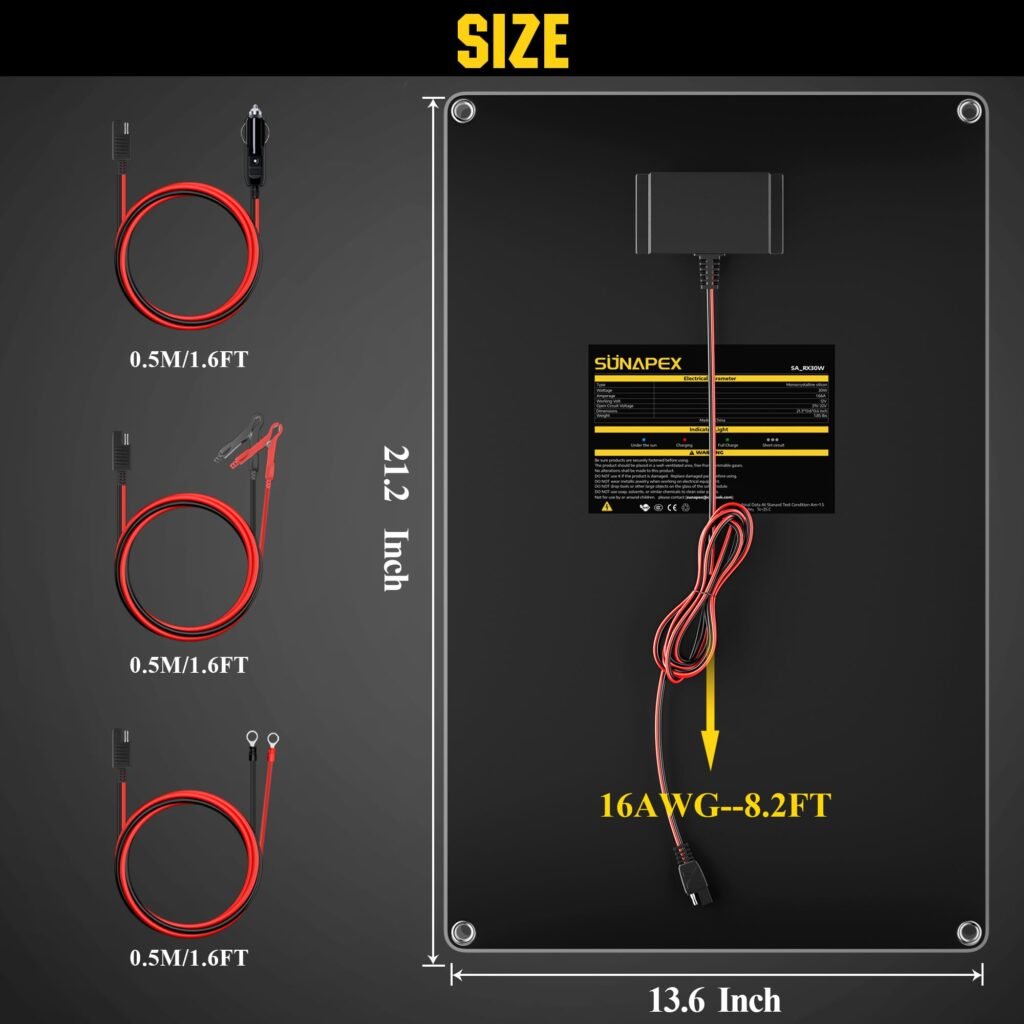
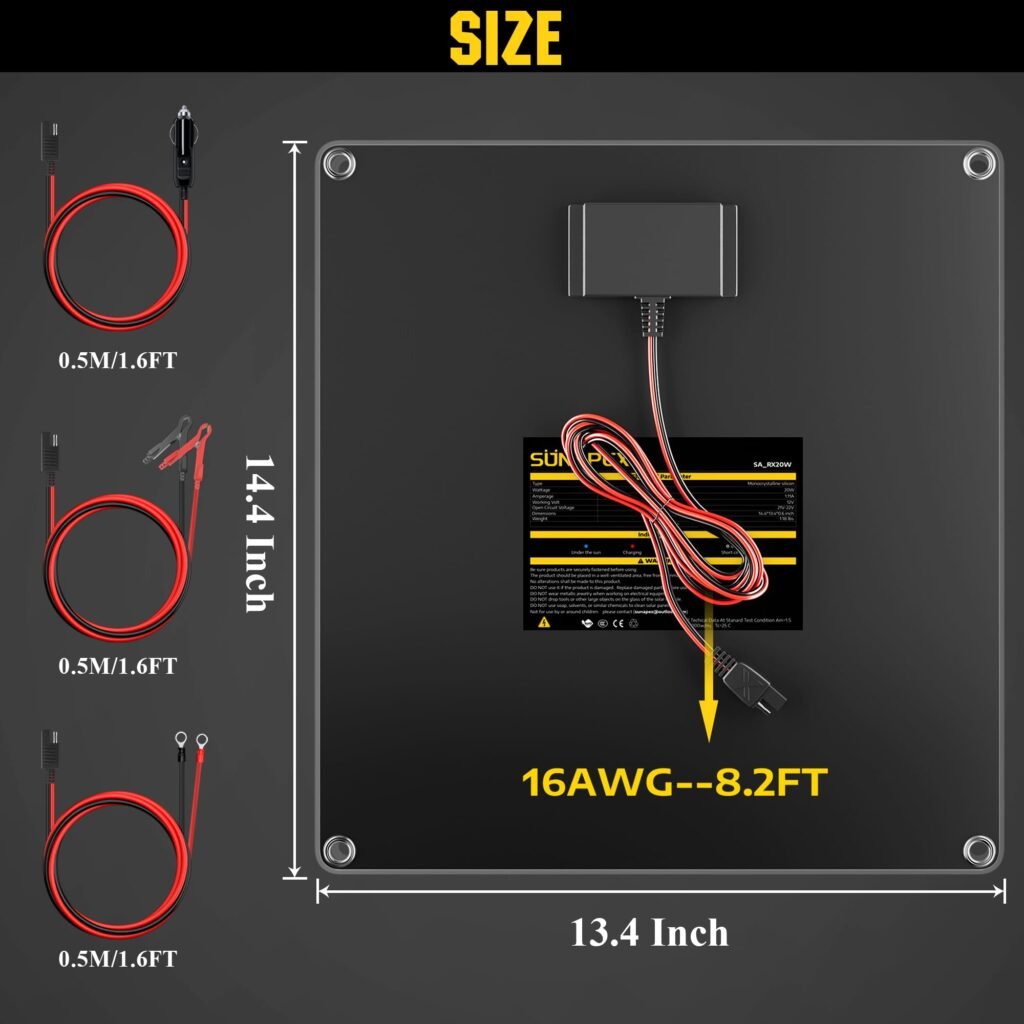
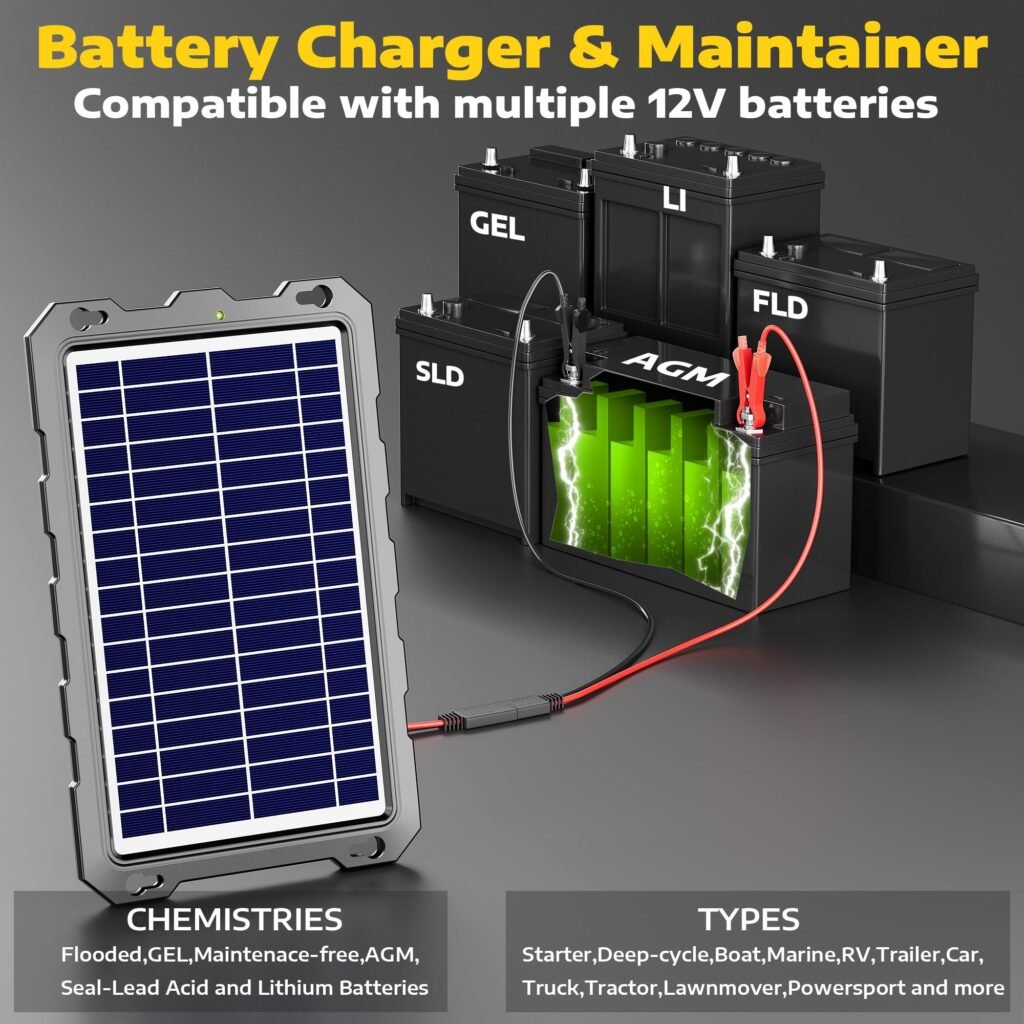
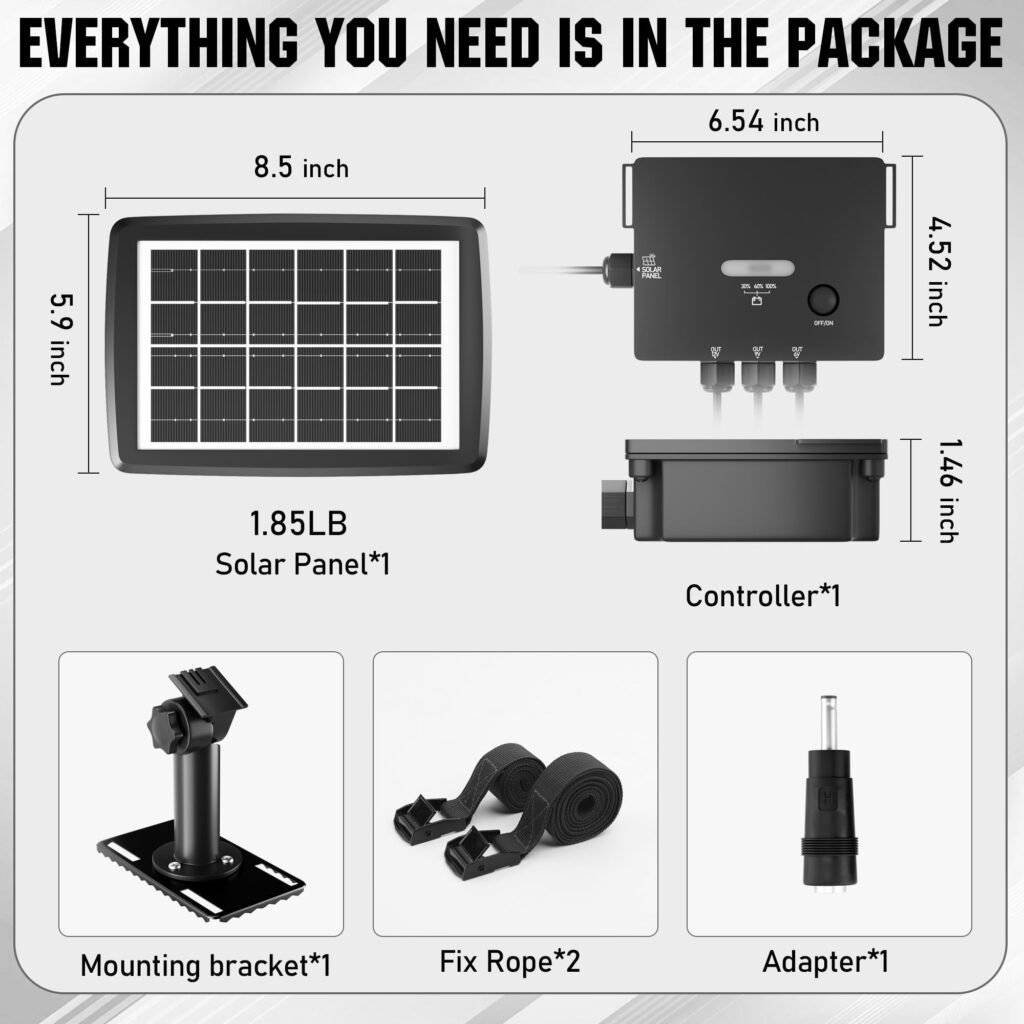
Solar Panel
The Environmental Impact of Switching to Solar Energy

In our climate changing era, solar energy is a game changer in the sense of the transition from continuous dependence on non renewable resources to one that will assist in combating climate change. Solar energy is a clean, plentiful power source that can help the planet. Learning of its impact on the environment will help individuals, businesses and governments to adopt this sustainable energy solution.
Reducing Carbon Emissions
There is no doubt about the most profound effect the extraction of solar energy can have: reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The traditional sources of energy, coal, oil, and natural gas, release enormous amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other pollutants into the atmosphere. The amount of carbon saved by the average household switching over to solar power is about 3,000 pounds, according to the U.S. Department of Energy.
In operation, solar panels are a zero emission energy source, since they generate electricity without combustion. Replacing fossil fuels with solar energy will help close the carbon gap and mitigate climate change, reduce pollution, clean the air and protect ecosystems from the negative impact of pollution.

Decreasing Water Usage
Traditionally, energy production can further complicate water scarcity, and it is a global growing concern. Reliance of power plants on fossil fuels or nuclear power means they come at the expense of huge water resources. Solar Energy systems, however, don’t need very much water, particularly photovoltaic (PV) panels.
Due to this reduced water dependency, solar energy is a good option for arid and drought prone areas to conserve water and at the same time generate clean electricity.
Land Degradation, Habitat Loss and Minimizing
Solar energy systems are simply different from how coal mining or natural gas extraction works – unlike them, they aren’t intrusive processes that degrade the land or destroy wildlife habitats. Agrivoltaics (solar farms with agriculture) is a way to integrate large solar power generation with crop cultivation. Also, rooftop solar uses existing infrastructure without additional land use needs.
They are also made greener with efforts to design solar farms that fit in with natural ecosystems. For example, pollinator friendly vegetation is planted below solar panels to help increase local biodiversity.
Reducing Air Pollution
Harmful pollutants released from the combustion of fossil fuels such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides and particulate matter all cause breathing diseases and cardiovascular diseases. When communities switch to solar energy solutions, they can improve air quality, and therefore public health.
The ability of solar energy to produce electricity without polluting is a fundamental approach to sustainable development and urban planning. Solar installations in cities can greatly decrease smog and enhance the quality of life of its residents.
Energy Waste Tackling with Efficient Systems
Specific energy needs can be met by design in solar energy systems which therefore avoid the inefficiencies of centralized power grids. Locally generated energy, including the most common distributed solar installations—rooftop panels—minimize transmission losses and make the process more efficient.
In addition, developments in solar technology mean that we can store any excess energy and use it, for example, in cases when there is low sunlight. This innovation enables us to rid ourselves of dependence on fossil fuel powered grid electricity and to strengthen our energy resiliency.
Recycling ; End of Life Management
While solar panels last around 25 to 30 years, their environmental impact doesn’t just begin at the date they’re installed. It is imperative to recycle properly and recycle waste at the end of life, to clean the environment and recover silicon, glass and metals.
Indeed, governments and manufacturers have invested increasingly in recycling, in order to ensure safe disposal of the solar panels. By reusing materials, these initiatives lower landfill waste and promote the circular economy, and they help with new solar products.

Energy Independence and Resilience (EIR)
As an avenue that propagates energy security and resilience, solar energy enables people and communities to decrease their dependency upon imported fossil fuels. Solar systems produce the electricity locally, eliminating many of the environmental costs associated with transportation and the distribution of energy.
Regions prone to natural disasters can have reliable power through solar energy, combined with battery storage- during grid outages. And it’s crucial because it’s getting harder to heal as climate change makes extreme weather events more frequent and more severe.
Supporting the development of Sustainable Economic Growth.
Sustainable economic growth comes from green jobs that promote the solar energy industry where innovation is driven. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) estimated that the solar sector employed around 4.3 million people worldwide in 2021.
Investing in solar energy would help countries stimulate local economies, improve their people’s situation and begin their transition towards a low carbon future. These offers provide clear evidence of the central role that solar energy has to play in sustainable development.
Overcoming Challenges
While many things are great about solar energy, the production of solar panels comes with an environmental impact or requires rare earth materials. Nevertheless, on-going research intends to find cleaner production methods and alternative materials to deal with them.
Solar energy is becoming cost effective with technological advancements, economies of scale, and there is a greater uptake across the world.
Conclusion
It is overwhelmingly positive when switching to solar energy. But solar energy can help curb carbon emissions and save water, foster biodiversity and improve the air we breathe. Together individuals and communities embrace solar solutions to a more clean, healthy, and more resilient world.
Solar power will most definitely be a key determining factor of what the future will look like when the global transition to renewable energy progresses at a faster pace. Whether through community solar projects, large scale solar farms or via residential installations, choosing to go solar is a major move to protect the environment for future generations.